IGMC standards 2.0, compiled by over 50 international experts who were convened by GFHS and UNEP, includes 12 principles, 84 indicators and corresponding strategies and measures with an authentication rating system to guide IGMC pilots planning and construction.
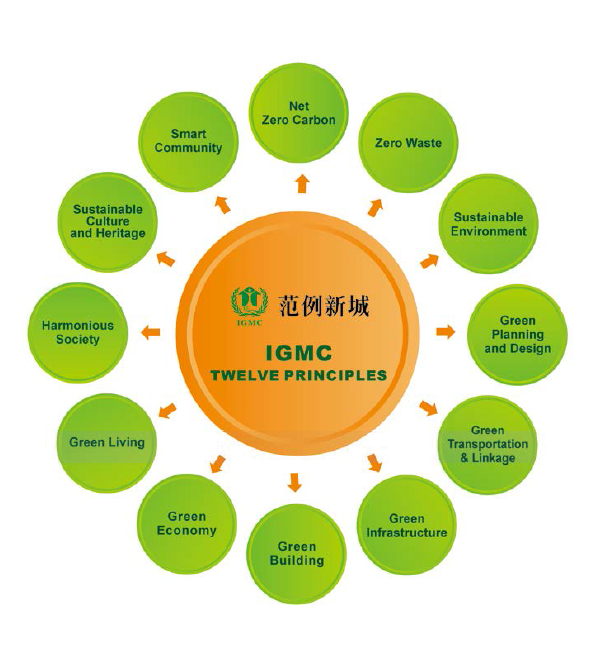
12 principles of IGMC include Net Zero Carbon, Zero Waste, Sustainable Environment, Green Planning + Design, Green Transportation and Linkages, Green Infrastructure, Green Building, Green Economy, Green Living, Harmonious Society, Culture and Heritage, Smart Community. These principles are consistent with the UN Habitat Agenda and Rio+20 resolution, andembody a commitment to sustainable cities and human settlements.
The year of 2016 marks a turning point for sustainable urban development around theglobe. Registering itself in the context of the new situation and the above global agreements in 2016, the IGMC Standards 3.0 was offcially released at the 11th Global Forum on Human Settlements (GFHS-XI) on 18 October 2016 as a parallel event of "Habitat III". The relevant experts and senior representatives from GFHS, UN-Habitat, UNEP and local governments attended the ceremony.
The vision of the IGMC standards 3.0 is based on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and New Urban Agenda, and concentrated on 6 Key principles: Safety, Sustainability, Equity, Identity, Prosperity, and Happiness, and is carried out through the 18 categories of the six dimensions of environment, spatial planning and development, economy, basic services, society and culture. Furthermore, the 18 categories are further elaborated in terms of definitions and aims, key strategies and methodologies, key indicators, scoring systems and best practices.
.jpg)
The Main Functions and Benefits of IGMC 3.0
Aiming at assessing and guiding sustainable urban development for both new and existing urban areas, the main functions and benefits of IGMC 3.0 include:
1. Guiding the overall process of urban sustainable development projects based on transit orientation and integrated planning by providing innovative concepts, integrated strategies and methodologies, benchmarks and monitoring framework for improved overall performance and efficient investment.
2. Appraising projects at planning or design phases to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement, avoiding various risks.
3. Assessing efficiency, inclusiveness, sustainability, and resilience of existing urban areas for comparison with others and to identify opportunities for improvement and transition to more sustainable cities and human settlements for all.
4. Providing the basis for decision-making from multi-scale levels of government especially from metropolitan and city-wide polices to strategies of sub-city districts and communities, promoting implementation of SDGs and New Urban Agenda through formulation of action plans and policy recommendations.
5. Providing a timely urban sustainable development manual for training for relevant stakeholders including mayors, urban managers, developers, planners,architects and engineers.
